What is Advance Tax
Advance Tax is the payment of tax in advance during the financial year in order to avoid lumpsum payments at the end of the year and also to avoid the interest imposed under sections 234B & 234C.
Who needs to pay Advance Tax?
As per Section 208 of the Income Tax Act, Advance tax shall be payable in a financial year by every person whose income tax liability is Rs.10,000/- or more as computed in accordance with the rates in force for the said financial year.
Applicable to :
- Salaried Individuals (if the tax liability exceeds Rs. 10,000 after considering the TDS deducted on salary and under other heads of income).
- Any person carrying on Business or Profession (even applicable to persons those opting for presumptive basis of income).
- Non-residents earning taxable income from India.
- Senior Citizens (60+ years) and whose income contains from business or profession.
Not Applicable to :
- Senior citizens who do not have income from business or profession.
- Persons whose tax liability is less than Rs.10,000/- after deducting TDS.
Income to consider for calculating Advance Tax
The income earned under the following heads are to be considered to calculate the advance tax liability
- Income under the head salary
- Income from House property
- Income from Business or Profession
- Income from Capital Gains (both short-term and long-term) and income should be considered quarter wise to avoid interest
- Income from other sources (such as interest income, dividend income (to be considered quarter wise), foreign income etc)
How to compute the tax liability?
Step 1: Estimate the total Income from all the heads of income.
Step 2: Calculate the tax liability based on the income tax rates in force.
The income tax rates for the F.Y 2025-26 are as follows:
| Income Tax Slab | Income Tax Rates |
|---|---|
| ₹ 0 – ₹ 4 lakhs | 0% |
| ₹ 4 lakhs- ₹ 8 lakhs | 5% |
| ₹ 8 lakhs- ₹ 12 lakhs | 10% |
| ₹ 12 lakhs – ₹ 16 lakhs | 15% |
| ₹ 16 lakhs – ₹ 20 lakhs | 20% |
| ₹ 20 lakhs- ₹ 24 lakhs | 25% |
| ₹ 24 lakhs & above | 30% |
Step 3: Deduct the TDS credit as reflected in your 26AS and eligible reliefs such relief under section 89, 90 or 91.
Step 4: Check if tax liability is greater than ₹ 10,000, if yes advance tax liability arises.
Step 5: Pay the advance tax on or before the due dates.
| Due Date | Instalment | Percentage of Tax |
|---|---|---|
| 15th June | 1st Instalment | 15% of tax |
| 15th September | 2nd Instalment | 45% of tax (cumulative) |
| 15th December | 3rd Instalment | 75% of tax (cumulative) |
| 15th March | 4th Instalment | 100% of tax (cumulative) |
Note: In case of persons having income under presumptive basis 100% of the tax for the presumptive income alone will be applicable in the 4th Instalment.
What happens if advance tax is not paid on due date?
If advance tax is not paid on due date interest under section 234B and 234C will be attracted.
Interest under section 234B will be attracted when 90% of the tax liability is not paid at the rate of 1% per month from 1st April of next financial year to the date of determination of the tax liability.
Interest under section 234C will be attracted when there is a shortfall of the tax amount paid for the said instalment in the following manner:
| Due Date | Rate of Interest & applicable months | Amount on which interest is to be calculated | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|
| 15th June | 1% for 3 months | Difference between the amount due and the amount paid | If 12% of the tax is paid as advance tax, the interest under this section will not be applicable. |
| 15th September | 1% for 3 months | Difference between the amount due and the amount paid till the 2nd Instalment | If 36% of the tax is paid as advance tax, the interest under this section will not be applicable. |
| 15th December | 1% for 3 months | Difference between the amount due and the amount paid till the 3rd Instalment | Interest will be applicable on the difference amount. |
| 15th March | 1% for 1 month | Difference between the amount due and the amount paid till the 3rd Instalment | Interest will be applicable on the difference amount. |
How to pay Advance Tax?
Step 1 : Visit the website of Income Tax (https://www.incometax.gov.in)
Step 2 : From the quick links select e-pay tax option.
Step 3 : Enter your PAN twice and Mobile number to proceed further.
Step 4 : Click on the Income Tax as shown below to proceed further.
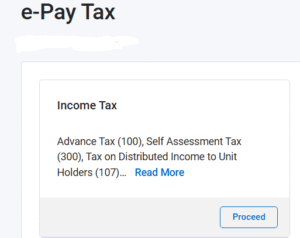
Step 5 : Select the Assessment year and Type of Payment and proceed further.
For example, if you are paying the advance tax for the Financial year 2025-26, from the assessment year drop down select 2026-27 and the Type of payment as Advance Tax.
Step 6 : The next step is enter the amount of advance tax to be paid in the Tax column and proceed further to the next screen to make payment.
Step 7 : In the next screen the mode of payment methods will be displayed such as Net Banking, Debit card, Pay at Bank Counter, RTGS/NEFT, Payment Gateway including UPI and credit card. Select any one of the method to make the payment.
Step 8 : A preview of the details entered will be displayed before making the payment as follows:
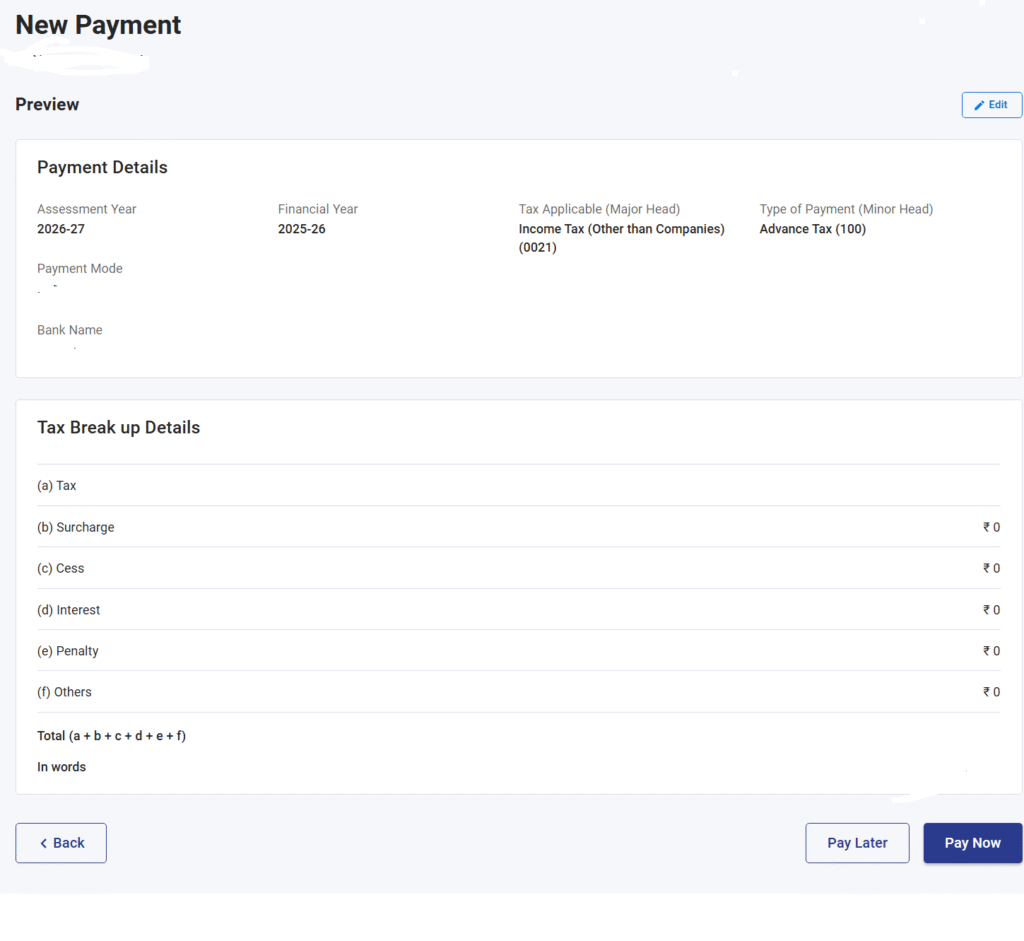
Step 9 : Click on Pay now to make the payment immediately.
Step 10: The acknowledgement will be generated with the payment details.
Conclusion
It is important to review the income earned during the year on a timely basis and also to determine the tax liability at the applicable rates for the financial year and to pay the advance tax within the due date to avoid lumpsum payment at the end and also to avoid interest payment at the time of filing the return of income.
📢 Now Offering Professional Tax Services!
We’re excited to announce the launch of our new Tax Services section! Whether it’s income tax filing, GST return support, or other compliance solutions, we’re here to help individuals, businesses, and NRIs navigate Indian tax systems with ease.
👉 Explore Our Tax Services

